-
Articles/Ads
Article ST. ALBAN'S ABBEY. ← Page 2 of 10 →
Note: This text has been automatically extracted via Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software.
St. Alban's Abbey.
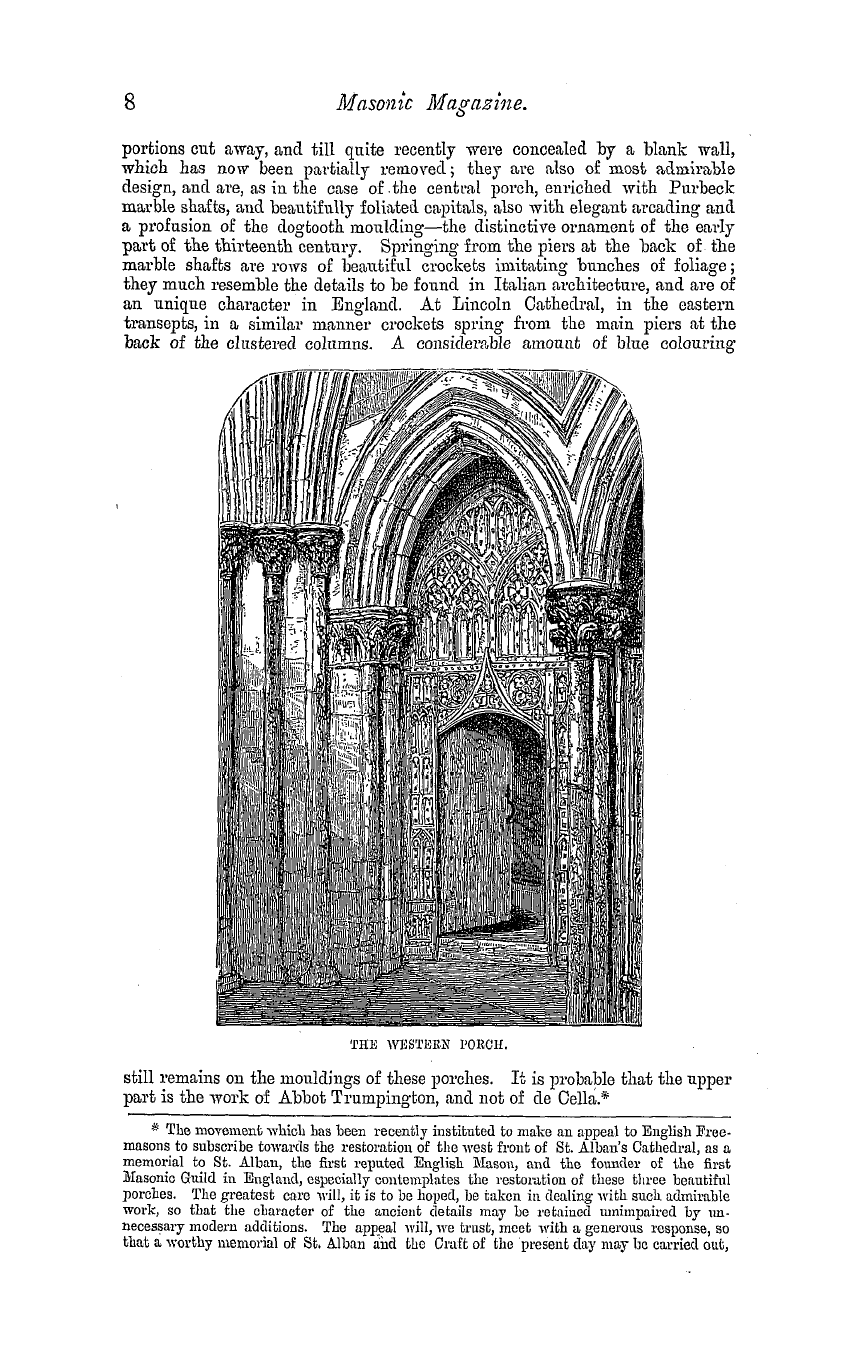
limited space will allow , the reader should refer to Buckler ' s "Abbey Church of St . Albans , " and to Nicholson ' s " Guide to St . Alban ' s Abbey ; " also to Bro . James Neale ' s most admirable and careful work , in which all the more important portions of the building are beautifully illustrated . This noble building furnishes admirable examples of every period of architecture . The walls are in great measure composed of Roman bricks and tiles
, taken from the walls of the adjoining town of Vernlamium , which had been carefully selected by the last Saxon Abbots in anticipation of the rebuilding of the Church . There are many other examples in England where Roman materials have been used for the constructive portions of earl y Ecclesiastical edifices , as at Brixworth , Northamptonshire , and St . Botolp h ' s Priory Church , Colchester . The earliest ornamental portion of the existing building is probabl
y to be found in the transepts , where , in the fcriforium , are to be seen a series of balusters of the Saxon type , which are said to have been preserved from the original Church of King Offa , when the Abbey was rebuilt by Abbot Paul in the year 1077 . This theory is to a certain extent supported by the fact that these balusters do not seem to fit into or belong to their present position , and they may therefore have been retained from the earlier building , though they
might very well belong to Abbot Paul ' s time , as similar balusters exist in two churches at Lincoln , which are know to have been built after the period of the Norman Conquest . Shortly after the battle of Hastings , the Abbot , by his opposition to William the Conqueror , fell into disgrace ; but Abbot Paul , of Caen , having been appointed in the year 1077 , at once commenced the rebuilding of the Church , on
a scale far grander than anything which had been previously attempted . Archbishop Lanfanc had already set the example by rebuilding the Cathedral at Canterbury , of which the crypt is still remaining , though it has been asserted that not a vestige of his work now exists , the Cathedral having been entirely rebuilt by Priors Ernul ph and Conrad , at the commencement of the twelfth century . Great works were also in progress at Norwich , Rochester , and Winchester Cathedrals , of whicli we have considerable remains at the present time , but the design carried out at St . Albans was of a more ambitious character than that of any of the co-eval buildings . *
The remains of Abbot Paul ' s work are the magnificent central tower , by far the grandest Norman tower in England ; the western portion of the north and south presbytery aisles , the transept choir and choir aisles to the west of the tower , and the six eastern bays on the north side of the nave . The architecture is of a massive and plain type , the walls being of great thickness , and the piers of unusual size ; the windows are also larger than are generally
found in Norman architecture . The tower arches are very lofty , and in the choir , nave , and transepts we have the usual arrangement of triforium and clerestory above the main arcade . The whole of this portion of the fabric , including the core of the piers , arches , & c ., is composed of Roman brick and tile , obtained from the old town of Vernlamium as above mentioned , as furnishing the most convenient quarry in a part of the country where no
building stone is to be obtained . The outer and inner surfaces seem to have been covered with a thin layer of plaster , ancl the inner walls and arches were probably adorned with decorative painting and masonry patterns , of which possibly there are some remains , though the extensive system of mural painting still existing on the Norman arches , etc ., was probably for the most part executed in the latter half of the twelfth or beginning of the thirteenth century . The next work in point of date is probably of the time of Abbot Robert de
Note: This text has been automatically extracted via Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software.
St. Alban's Abbey.
limited space will allow , the reader should refer to Buckler ' s "Abbey Church of St . Albans , " and to Nicholson ' s " Guide to St . Alban ' s Abbey ; " also to Bro . James Neale ' s most admirable and careful work , in which all the more important portions of the building are beautifully illustrated . This noble building furnishes admirable examples of every period of architecture . The walls are in great measure composed of Roman bricks and tiles
, taken from the walls of the adjoining town of Vernlamium , which had been carefully selected by the last Saxon Abbots in anticipation of the rebuilding of the Church . There are many other examples in England where Roman materials have been used for the constructive portions of earl y Ecclesiastical edifices , as at Brixworth , Northamptonshire , and St . Botolp h ' s Priory Church , Colchester . The earliest ornamental portion of the existing building is probabl
y to be found in the transepts , where , in the fcriforium , are to be seen a series of balusters of the Saxon type , which are said to have been preserved from the original Church of King Offa , when the Abbey was rebuilt by Abbot Paul in the year 1077 . This theory is to a certain extent supported by the fact that these balusters do not seem to fit into or belong to their present position , and they may therefore have been retained from the earlier building , though they
might very well belong to Abbot Paul ' s time , as similar balusters exist in two churches at Lincoln , which are know to have been built after the period of the Norman Conquest . Shortly after the battle of Hastings , the Abbot , by his opposition to William the Conqueror , fell into disgrace ; but Abbot Paul , of Caen , having been appointed in the year 1077 , at once commenced the rebuilding of the Church , on
a scale far grander than anything which had been previously attempted . Archbishop Lanfanc had already set the example by rebuilding the Cathedral at Canterbury , of which the crypt is still remaining , though it has been asserted that not a vestige of his work now exists , the Cathedral having been entirely rebuilt by Priors Ernul ph and Conrad , at the commencement of the twelfth century . Great works were also in progress at Norwich , Rochester , and Winchester Cathedrals , of whicli we have considerable remains at the present time , but the design carried out at St . Albans was of a more ambitious character than that of any of the co-eval buildings . *
The remains of Abbot Paul ' s work are the magnificent central tower , by far the grandest Norman tower in England ; the western portion of the north and south presbytery aisles , the transept choir and choir aisles to the west of the tower , and the six eastern bays on the north side of the nave . The architecture is of a massive and plain type , the walls being of great thickness , and the piers of unusual size ; the windows are also larger than are generally
found in Norman architecture . The tower arches are very lofty , and in the choir , nave , and transepts we have the usual arrangement of triforium and clerestory above the main arcade . The whole of this portion of the fabric , including the core of the piers , arches , & c ., is composed of Roman brick and tile , obtained from the old town of Vernlamium as above mentioned , as furnishing the most convenient quarry in a part of the country where no
building stone is to be obtained . The outer and inner surfaces seem to have been covered with a thin layer of plaster , ancl the inner walls and arches were probably adorned with decorative painting and masonry patterns , of which possibly there are some remains , though the extensive system of mural painting still existing on the Norman arches , etc ., was probably for the most part executed in the latter half of the twelfth or beginning of the thirteenth century . The next work in point of date is probably of the time of Abbot Robert de